Serial Peripheral Interface Using Vhdl
UART, Serial Port, RS-232 Interface Code in both VHDL and Verilog for FPGA Implementation. Do you know how a UART works? If not, first brush up on the basics of UARTs before continuing on.
- Serial Peripheral Interface Standard
- Serial Peripheral Interface Tutorial
- Serial Peripheral Interface Protocol
- Serial Peripheral Interface Specification
Serial Peripheral Interface Standard
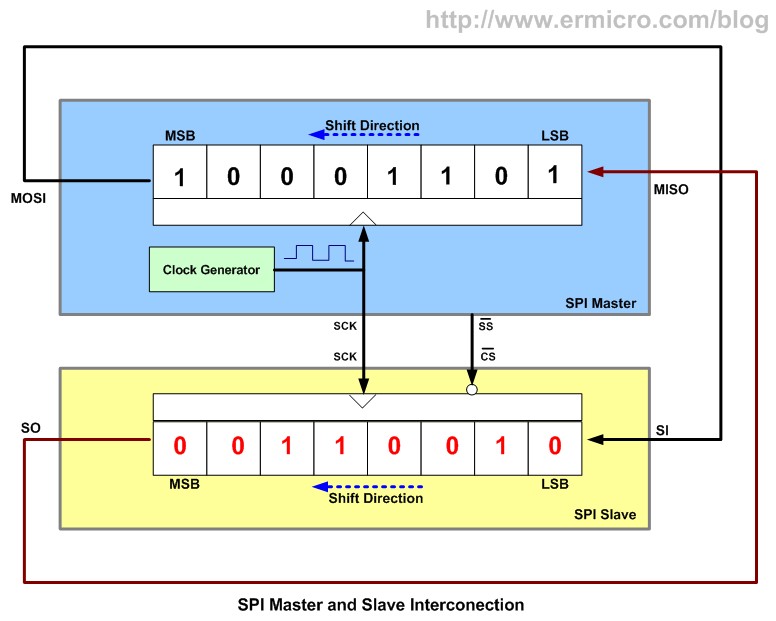
Single master to single slave: basic SPI bus example The Serial Peripheral Interface ( SPI) is a interface specification used for short distance communication, primarily in. The interface was developed by in the mid 1980s and has become a. Typical applications include cards. SPI devices communicate in mode using a architecture with a single master. The master device originates the for reading and writing. Multiple slave devices are supported through selection with individual (SS) lines. Sometimes SPI is called a four-wire serial bus, contrasting with,, and serial buses.
More importantly, Wave of Mutilation boasts 23 songs, as opposed to the 17 on the best-of disc on Death to the Pixies. While, theoretically, 23 tracks should be enough to capture most, if not all, of the band's definitive moments, that's not quite the case here. Discover releases, reviews, credits, songs, and more about Pixies - Best Of Pixies (Wave Of Mutilation) at Discogs. Complete your Pixies collection. Pixies wave of mutilation best of pixies rarlab. Pixies Wave Of Mutilation Best Of Pixies Rarlab. Buy Wave of Mutilation - The Best of the Pixies at Amazon. Wave of Mutilation: Best of Pixies is an effort at capturing some of the Pixie's greatest.
Serial Peripheral Interface Tutorial
The SPI may be accurately described as a synchronous serial interface, but it is different from the (SSI) protocol, which is also a four-wire synchronous serial communication protocol. SSI Protocol employs and provides only a single channel. A typical hardware setup using two to form an inter-chip To begin communication, the bus master configures the clock, using a frequency supported by the slave device, typically up to a few MHz. The master then selects the slave device with a logic level 0 on the select line. If a waiting period is required, such as for an analog-to-digital conversion, the master must wait for at least that period of time before issuing clock cycles.
Serial Peripheral Interface Protocol
During each SPI clock cycle, a full duplex data transmission occurs. The master sends a bit on the MOSI line and the slave reads it, while the slave sends a bit on the MISO line and the master reads it. This sequence is maintained even when only one-directional data transfer is intended. Transmissions normally involve two shift registers of some given word size, such as eight bits, one in the master and one in the slave; they are connected in a virtual ring topology. Data is usually shifted out with the most-significant bit first.
Serial Peripheral Interface Specification
On the clock edge, both master and slave shift out a bit and output it on the transmission line to the counterpart. On the next clock edge, at each receiver the bit is sampled from the transmission line and set as a new least-significant bit of the shift register. After the register bits have been shifted out and in, the master and slave have exchanged register values. If more data needs to be exchanged, the shift registers are reloaded and the process repeats. Transmission may continue for any number of clock cycles. When complete, the master stops toggling the clock signal, and typically deselects the slave. Transmissions often consist of 8-bit words.